Post Time: 2025-07-26
Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in our overall health, and maintaining healthy ranges is essential for optimal functioning. The ideal blood sugar range varies depending on several factors such as age, sex, and lifestyle. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the normal blood sugar range for adults with no underlying medical conditions is between 70-99 mg/dL after an overnight fast.
Managing Blood Sugar Fluctuations: A Delicate Balance
The fluctuations in our blood sugar levels are influenced by various factors including diet, exercise, stress, and sleep. When we eat a meal or snack that's high on the glycemic index (GI), it can cause a rapid spike in our blood sugar levels. Conversely, consuming low-GI foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables helps maintain stable blood sugar ranges.
Achieving Stability through Diet: A Closer Look
The food we eat plays an instrumental role in regulating our blood sugar levels. Including fiber-rich foods like legumes, cruciferous veggies, and nuts can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and release glucose gradually into the bloodstream. Furthermore, avoiding refined sugars and saturated fats helps maintain insulin sensitivity.
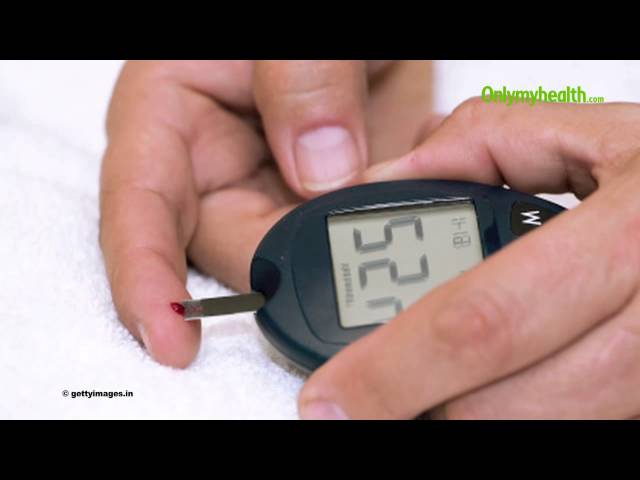
Staying on Top: Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring your blood sugar ranges at home using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system is vital for understanding fluctuations in your levels. This will also allow you to track how different foods affect your numbers, making it easier to develop an individualized meal plan.
The Connection Between Stress and Blood Sugar Levels
Stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol into our bloodstream. These hormones increase glucose production by gluconeogenesis and disrupt insulin action in peripheral tissues leading to higher blood sugar levels. Furthermore, chronic stress can lead to metabolic syndrome, characterized by increased body mass index (BMI), high triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, hypertension, and hyperglycemia.
Navigating a Pathway towards Healthy Blood Sugar Ranges
Achieving and sustaining healthy blood sugar ranges is crucial for reducing the risk of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes complications like cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve disorders. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels through regular physical activity also enhances mental well-being by preventing anxiety and depression.
Supplements Supporting a Healthy Blood Sugar Range: A Guide
Vitamins and minerals such as chromium picolinate can help reduce fasting glucose concentrations in individuals with insulin resistance syndrome when combined with diet therapy according to research findings. Alpha-lipoic acid has been shown in studies to improve peripheral neuropathy symptoms associated diabetes; vitamin D is considered vital for overall well-being but may not have any effects on blood sugar management itself.
Blood Sugar, Exercise and the Connection: Time to Move
Regular physical activity plays a significant role in maintaining insulin sensitivity. Activities like yoga can help individuals reduce their body mass index which also aids glucose uptake into muscle cells improving insulin action within an hour of mealtime for up to four days afterward making sustained blood sugar regulation more achievable long-term.
Healthy Blood Sugar Ranges and Mental Clarity: The Connection Uncovered
Balanced diet coupled alongside with daily moderate activity significantly lowers stress hormone secretion; therefore, it's no surprise that individuals whose glucose is consistently within acceptable limits enjoy reduced anxiety symptoms. Their mind also functions better due to enhanced insulin sensitivity allowing proper glucose absorption which helps prevent brain-fog caused by high blood sugar.
Unlocking Healthy Blood Sugar Ranges for Long-Term Success
Monitoring your blood levels through various methods mentioned earlier can reveal any anomalies or issues with how you are managing stress overall - maintaining physical activity combined healthy diet practices is key.
For Similar Videos Click Normal Blood glucose is less than 100 mg per decilitre. If the blood glucose is more than 100 -- 125 mg per decilitre then it is called as pre-diabetes or impaired fasting glucose. If the blood glucose is more than 126 mg per decilitre in fasting can splenda raise blood sugar glucose or 180 mg per decilitre postoperative state this is called diabetes. According to inter heart study where 50,000 people from 55 countries were studied, diabetes was one of the how to get blood sugar down fast naturally main risk factor that leads to developing heart attack as diabetes causes changes in the cellular molecules and protein molecules. In India people home remedy for blood sugar have high incidence of diabetes. Watch this video to know more how blood glucose affects the heart attack.