Post Time: 2025-07-26
When it comes to maintaining good health, one of the most critical factors is managing your blood sugar levels. High or low blood sugar can have severe consequences on both physical and mental well-being.
The normal blood sugar range for adults varies, typically ranging from 70-99 mg/dL after an overnight fast. However, this can fluctuate depending on several factors such as diet, exercise, stress levels, and sleep quality. To maintain a stable blood sugar level, it is essential to understand what causes fluctuations in your range.
The Science Behind Normal Blood Sugar Range Explained
Insulin sensitivity plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels. When you consume food that contains carbohydrates, it triggers an increase in glucose release into the bloodstream. In response, insulin is released from the pancreas to facilitate the uptake of this excess glucose by cells throughout your body. However, when your body becomes resistant to insulin due to various factors like obesity or genetics, blood sugar levels remain high.
Insulin resistance can lead to persistent high blood sugar, increasing diabetes risk and associated complications such as cardiovascular disease and nerve damage. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial in improving insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
Maintaining Optimal Blood Sugar Levels
While genetics play a significant role in determining your natural metabolism rate, there are several lifestyle factors that significantly impact blood sugar levels:
- Monitoring techniques: Measuring blood glucose using glucometers or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) helps track daily patterns. These devices enable timely adjustments to eating habits and physical activity.
- Dietary choices: Consuming foods high in fiber can help slow down the release of carbohydrates into the bloodstream, leading to more stable blood sugar levels.
Exercise's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Regular physical activity has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity. Engage in at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic exercises or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity exercise throughout your lifetime. Incorporating strength training is also beneficial, as it helps maintain muscle mass.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) sessions have emerged as a particularly effective way to improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
The Importance of Stress Management
Stress triggers an increase in cortisol levels, leading to increased glucose release from stored energy sources. This rise is then followed by decreased glucose uptake into cells due to a negative impact on insulin sensitivity.
To effectively manage blood sugar fluctuations, incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation and yoga into your daily routine.
The Role of Sleep Quality
Sleep deprivation has been shown to increase cortisol levels in the body. Consequently, this leads to higher glucose release from stored energy sources, causing blood sugar spikes. Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining stable insulin sensitivity.
Aim for 7-9 hours of continuous undisturbed sleep each night and prioritize developing a relaxing bedtime routine that prepares your body and mind for restful slumber.
Achieving a Sustainable Healthy Blood Sugar Range
Combining these strategies ensures long-term blood sugar control, reducing the risk associated with persistent high or low levels. Regular tracking of blood glucose using devices like glucometers can provide valuable insights into daily patterns.
Maintaining an optimal healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet are foundational for regulating insulin sensitivity.
By committing to this holistic approach to managing your body's internal ecosystem, you take significant steps towards optimizing health outcomes.
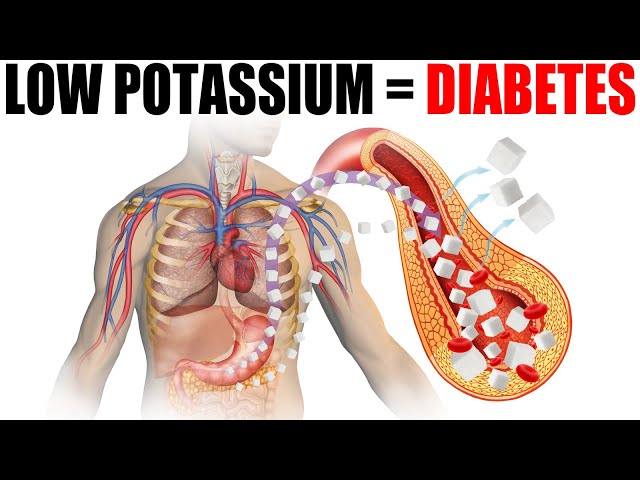
Download My FREE guide: First Signs of a Nutrient Deficiency 👉 Did you know that potassium deficiency could trigger diabetes? Learn more about the importance of potassium for diabetes and high blood pressure. DATA: 0:00 Introduction: Potassium and diabetes 0:15 Blood pressure medications and diabetes 2:47 Potassium benefits 3:45 Potassium RDAs 4:02 Foods high in potassium 5:45 Type 1 diabetes and potassium 6:33 Learn more about potassium! Today we're going to talk about how potassium affects diabetes and high blood pressure. Diuretics are commonly used to treat high blood pressure. But, they come with side effects, including an increased risk of developing diabetes. On the flip side, ace inhibitors, also used to treat high blood pressure, protect against diabetes and lower the risk of diabetes. I believe the big difference between these two drugs, when it comes to diabetes risk, is what they do to potassium. Diuretics deplete potassium, and without enough potassium, insulin can't be released very well. A deficiency of insulin can then lead to diabetes. Ace inhibitors increase potassium by helping to prevent the loss of potassium. So why do we even need a drug—why aren't we just consuming more potassium? Many people support healthy blood pressure and healthy blood sugar levels by taking potassium. Benefits of potassium: • It protects the kidneys • It protects the heart • It helps protect against stroke • It helps protect against diabetes • It helps power the nervous system in connection with the muscles • It helps regulate sodium The RDAs for potassium are 4700 mg. It might surprise you, but bananas aren't a good source of potassium. A few of the best sources of potassium are: • Leafy greens • Potatoes • Avocado • Electrolyte powder Dr. Eric Berg 324 blood sugar DC Bio: Dr. Berg, age is 104 normal blood sugar 58, is a chiropractor who specializes in Healthy Ketosis & Intermittent Fasting. He is the author of the best-selling book The Healthy Keto Plan, and is the Director of Dr. Berg Nutritionals. He no longer practices, but focuses on health education through social media. Follow Me blood sugar how long after eating On Social Media: Facebook: Instagram: TikTok: Disclaimer: Dr. Eric Berg received his Doctor of Chiropractic degree from Palmer College of Chiropractic in 1988. His use of “doctor” or “Dr.” in relation to himself solely refers to that degree. Dr. Berg is a licensed chiropractor in Virginia, California, and Louisiana, but he no longer practices chiropractic in any state and does not see patients so he can focus on educating people as a full time activity, yet he maintains an active license. This video is for general informational purposes only. It should not be used to self-diagnose and it is not a substitute for a medical exam, cure, treatment, diagnosis, and prescription or recommendation. It does not create a doctor-patient relationship between Dr. Berg and you. You should not make any change in your health regimen or diet before first consulting a physician and obtaining a medical exam, diagnosis, and recommendation. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. #keto #ketodiet #weightloss #ketolifestyle Thanks for watching! I hope this helps increase your awareness of the importance of potassium for diabetes and high blood pressure. I'll see you in the next video.