Post Time: 2025-07-26
Blood sugar levels are a crucial aspect of overall health, and maintaining stable blood sugar ranges is essential for preventing various diseases. Understanding what contributes to fluctuations in your blood sugar range can help you take proactive steps towards achieving optimal health.
Balancing Act: The Science Behind Normal Blood Sugar Ranges
When it comes to healthy living, the ideal blood sugar range serves as a benchmark against which our bodies measure overall well-being. For adults without diabetes, normal fasting glucose levels typically fall between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Ingesting carbohydrates or other forms of sugar causes insulin production in response to rising blood sugar, so maintaining balance is key.
Dietary Decisions: Navigating the World of Blood Sugar-Stabilizing Foods
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing and regulating our bodies' natural responses to food. Fiber-rich foods such as oats, broccoli, carrots are beneficial for their capacity to slow down glucose absorption into the bloodstream thereby stabilising blood sugar levels.
Managing Stress: The Unseen Connection Between Blood Sugar and Mental Health
Stress affects more than just mental well-being; it can have a profound impact on our bodies' ability to regulate blood sugar. When we feel stressed, cortisol is released which further increases blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis in the liver - an effect that must be monitored closely.
The Exercise Effect: How Regular Physical Activity Supports Healthy Blood Sugar Ranges
Exercising regularly can have a significant impact on our overall health and well-being by supporting healthy weight management reducing stress. When you exercise, your body becomes more responsive to insulin which allows glucose to get absorbed from the bloodstream thereby ensuring that blood sugar levels are maintained within normal limits.
Why Monitoring Your Blood Sugar Range Matters
Monitoring your progress is essential for making informed decisions about how best to manage and stabilize your blood sugar ranges - whether this involves tweaking what you eat, getting active or finding ways to reduce stress in our lives.
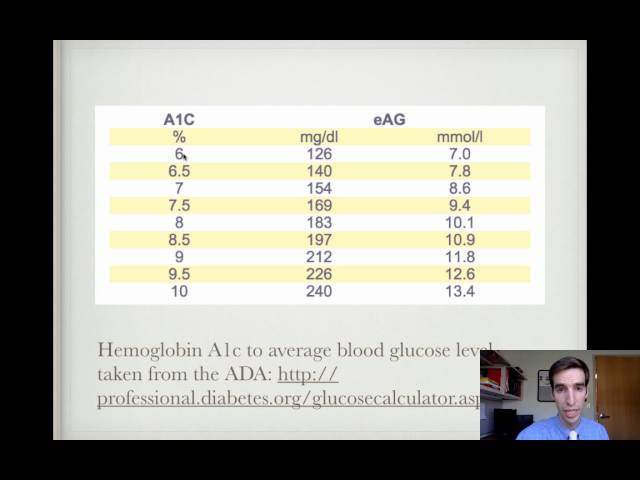
The Rule of Thomas for Hemoglobin A1c Conversion I love medical eponyms! Is it a delusion of grandeur to think that I could have a medical eponym of my own? Perhaps, but I will try regardless - please take my self-aggrandizement cum grano salis. Without further ado, I present: "The Rule of Thomas" for quickly calculating average which is worse low or high blood sugar blood glucose levels from Hemoglobin A1C percentages. Use the following formula: Average Blood Glucose = 120 mg/dL + 30 (HgbA1C% - 6%) Plug in your variable, namely the Hemoglobin A1C Percentage, and solve the equation. You will be left with an average blood glucose. For example, your 30 year old patient with type can dizziness be caused by high blood sugar 1 diabetes typically has excellent control of their blood sugar. Because your patient is young and healthy, you encourage them to maintain tight glucose control. You order a blood draw and obtain a hemoglobin A1C level of 6.5%. You would then have to use a table to find what their average blood glucose would be, but if you use the Rule of Thomas, you will be able to calculate the average blood glucose quickly. Average Blood Glucose = 120 mg/dL + 30 (6.5% - 6%) Average Blood Glucose = 120 mg/dL + 30 (0.5%) Average Blood Glucose = 120 mg/dL + 15 mg/dL Average Blood Glucose = 135 mg/dL As another example, you have a 58 year old male with type 2 diabetes that is newly diagnosed and poorly controlled. His hemoglobin A1C level prior to treatment is 12%. Using the formula: Average Blood Glucose = 120 mg/dL + 30 (12% - 6%) Average Blood Glucose = 120 mg/dL + 30 (6%) Average Blood Glucose = 120 mg/dL + 180 mg/dL Average Blood Glucose = 300 mg/dL As the medical community moves to patient-centered approaches to managing chronic illness, The Rule of Thomas is an easy way for clinicians and patients to understand and work with Hemoglobin A1c levels and their sugar free tigers blood correlating average blood glucose levels. The Rule of Thomas will help patients and clinicians communicate more easily about hemoglobin A1c and glucose levels. #bloodsugar #diabetes #diabetesmellitus #type2diabetes #bloodglucose #hemoglobinA1c #medicine #clinic #hospital #medicaleponyms #RuleofThomas #endocrine #endocrinology #medicaleducation #patientcentered #patientcommunication Key Links: Translating the A1C Assay Into Estimated Average Glucose Values: ADA Hemoglobin A1c to Average Glucose Level: Mayo Clinic Hemoglobin A1c conversion chart: